Human spaceflight is almost as old as space exploration due to the challenge and novelty of the environment, extensive screening and testing of candidates is required
The Beginning: Those accepted to become an astronaut, report to Houston, Texas, It is NASA’s Primary astronaut training facility. Today, it is known as the Johnson Space Center (JSC ) . It was established in 1961 as the Manned Spacecraft Center. In 1973, its name was changed to honor former president and Texas native Lyndon B.Johnson, who died that January. The JSC played an important role in the Gemini, Apollo, Skylab, space shuttle, and International Space Station programs. Over the course of its history, JSC has trained more than 300 US astronauts and 50 astronauts from other countries. The training process used today is the result of this significant experience.
Major Players: In the 1960s, the space club only included Russia and the USA. Later, the pool of human space flight-faring nations grew. Today, it still includes the USA (NASA) and Russia (Roscosmos ). However, it has grown to also include, Europe (ESA), JAPAN (JAXA ), CHINA (NSA ), And India ( ISRO ) . Outside government agencies, this list will also soon include passengers of space tourism.
Selection Process: The selection process for candidates has become more and more detailed and targeted as human spaceflight capabilities have grown . Spaceflight began as the selection of military fighters and test pilots in the 1960s. There was a considerable focus on physical capability. it has now evolved into a search for aptitude in engineering, sciences, life science, and mathematics. These will also continue to evolve in stride with human spaceflight capabilities as well as each nation’s individual objective.
Current Training Modules: Currently, Astronauts are only trained to fly in the Soyuz and live on the board ISS as these are the only space shuttle and stations available .
Training In Space: On the ISS, Astronauts are involved in assembly and orbit operations. This includes, but is not limited to, EVAs, Robotics operations using remote manipulators, experiment operations, and ISS maintenance tasks. They are, thus, trained in a simulated microgravity environment to prepare them for these tasks in space .
Theoretical Training: It is essential for astronauts to have in-depth knowledge of ISS and its Subsystems. They must know operational characteristics, mission requirements, objectives, and supporting systems and equipment for each experiment on their assigned missions. As a result, the long-duration missions aboard the ISS that last from there to six months take about two to three years of increment-specific training.
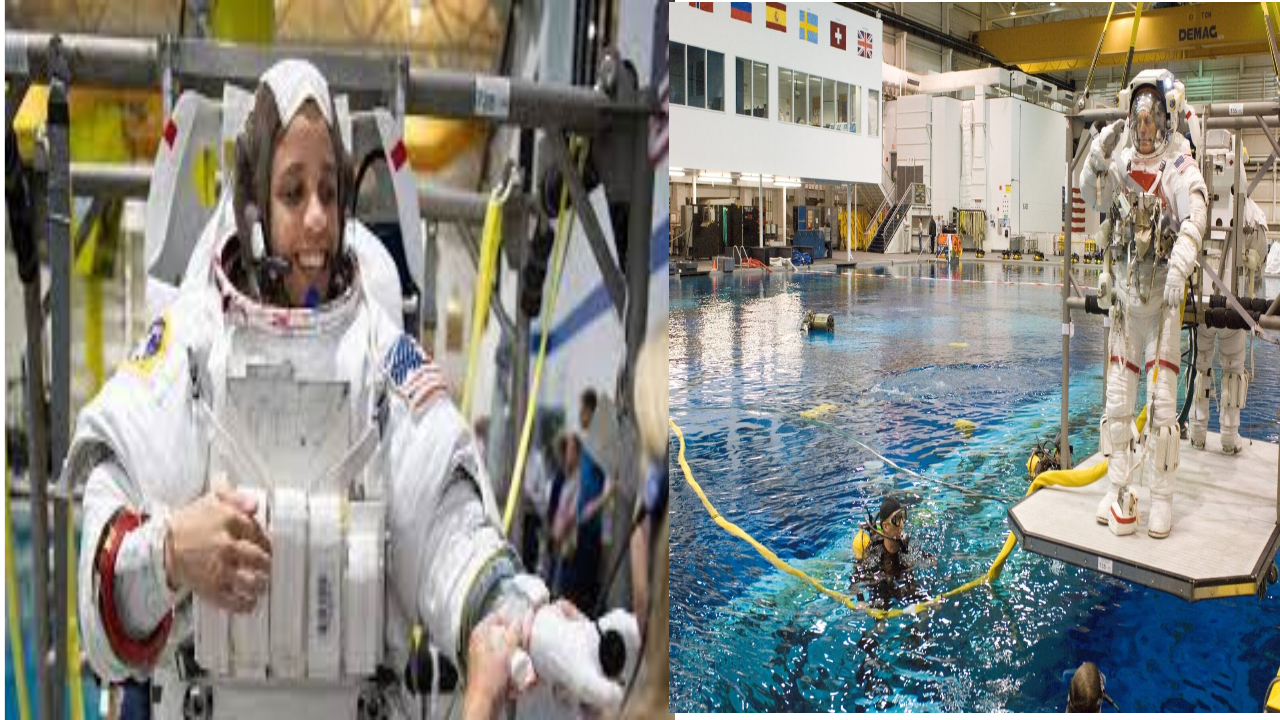
Training Facilities: Astronauts have to be prepared for general space travel and for their specific mission. In order to prepare them for the same.NASA has several locations for astronaut training . These are some of the training facilities.
· The Jake Garn Training Facility: This facility at JSC Houses a functional space station simulator, which makes astronauts familiar with the in-orbit laboratory systems of the international space station before they go there in person.
· The Space Vehicle Mockup Facility (SVMF ) . This facility consists of components that prepare astronauts for station operations. The Space Station Mockup And Training Facility ( SSMTF ) is a complete imitation of the ISS, Providing as much realism as possible to match conditions that will be experienced upon the orbiting space station.
· The Virtual Reality (VR) Laboratory: Here, Astronauts preparing for spacewalks or robotic arm operations test their skills. In a simulated microgravity environment generated by powerful computers, astronauts –each wearing special gloves, video display helmet, chest pack, and a controller-learn how to orient themselves in outer space, where up and down are vague, and even negligible corrections with thrusters can send someone spinning off into space .
ASTRONAUTS SPACESUITS: A spacesuit serves the purpose of protecting an astronaut in an environment where his/her body cannot sustain itself. The outer space environment calls for a special suit to protect people going into the deep realms of a territory that one cannot survive in without special protection. It is here that spacesuits come into action.
The need for spacesuits: Spacesuits help astronauts in several ways. They protect the people entering into space from getting very hot or cold. They also give astronauts oxygen to breathe, while they are working in space. They hold water to drink and also prevent astronauts from being harmed by space dust. Space dust may not sound very dangerous but when it moves at a very high speed, it can hurt someone. The suits even have special gold-lined visors to protect the eyes from bright sunlight.
Parts of a spacesuit: It is made up of several parts. One part covers the astronaut’s chest and the other connects to the gloves .there is a helmet that protects the head. The third part covers the legs and feet. Some parts of the suit are made of various layers of material. Each layer serves a different purpose. Some keep oxygen in the suit whereas others protect from space dust. Below the suit, astronauts wear another piece of clothing that covers their body except for fro the head, hands, and feet. Tubes are woven into it and water flows through these tubes to keep the astronauts cool
On the back, there is a backpack. It holds oxygen for the purpose of breathing. It eliminated the carbon dioxide that is breathed out. It also supplies electricity for the suit. A fan moves the oxygen through the spacesuit and a water tank holds the cooling water. The back of the suit also has a tool called SAFER. It has several small thruster jets. If an astronaut drifts away from the space station, he or she could the SAFER to fly Back.
Mobility In The Suit: It is difficult to move with an inflated space suit. It is like trying to move your fingers in a rubber glove blown up with air; it does not ensure much movement. To counter this difficulty, these suits are equipped with special joints or tapers in the fabric to help the astronauts bend their hands, arms, legs, knees, and ankles.
Communications: Space suits have radio transmitters/receivers so that spacewalking astronauts can talk with ground controllers and or other astronauts.
Modern Space Suit: EMU: Today’s Extravehicular Mobility Unit ( EMU ) is made up of a combination of soft and hard components to provide support, mobility, and comfort. This suit has 13 layers of material, including an inner cooling garment (two layers ), pressure garment (two layers ), thermal micrometeoroid garment ( eight layers ), and outer cover ( one layer ).The materials used include : nylon,Dacron,neoprene-coated nylon,mylar,gortex,Kevlar (materials used in bullet-proof vests ) and Nomex. All these layers are sewn and joined together to form the suit In contrast to early space suits, which were individually tailored for each astronaut.the EMU has component pieces of varying sizes that can be put together to fit the size of any given astronaut.
Extravehicular Visor Assembly (EVA ): The EVA fits over the helmet .it has the following pieces :
· A metallic–gold–covered visor to filter the sunlight
· A clear , impact-resistant cover for thermal and impact protection
· Adjustable blinders to block sunlight
· Four headlamps
· A TV camera
· In- Suit Drink Bag
Astronauts working in a space suit for up to seven hours need water . Therefore,it has the IDB, Which is a plastic pouch mounted inside the Helmet.